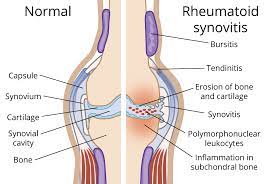
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, primarily affecting the joints. While the exact cause of RA is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic markers are associated with an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Individuals with a family history of RA might be more susceptible to the condition.
- Autoimmune Response: In individuals with a genetic predisposition, environmental triggers like infections or other factors might cause the immune system to malfunction. Instead of protecting the body, the immune system attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.
- Inflammation: The immune system’s attack on the synovium leads to chronic inflammation. This inflammation can cause joint damage, pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Synovial Changes: Inflammation in the synovium can lead to abnormal growth of tissue, forming a pannus. The pannus can invade and damage cartilage and bone within the joint.
- Cytokines: Cytokines are proteins produced by immune cells. In individuals with RA, certain cytokines contribute to inflammation and joint damage.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental triggers, such as infections, smoking, and exposure to certain pollutants, might play a role in triggering the autoimmune response in genetically susceptible individuals.
- Hormones: Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or menopause, can influence the activity of the immune system and impact the severity of RA symptoms.
It’s important to note that rheumatoid arthritis is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors. While researchers have made significant progress in understanding its underlying mechanisms, there is still ongoing research to uncover more details about the causes of RA. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to minimizing the impact of the disease on joint health and overall quality of life.
If you suspect you have rheumatoid arthritis or have been diagnosed with it, consulting a rheumatologist or healthcare provider is recommended for appropriate treatment and guidance. For More information, contact Dr. Bipin Shah, Ophthalmologist in Matunga. Visit Shanta Medical Centre.