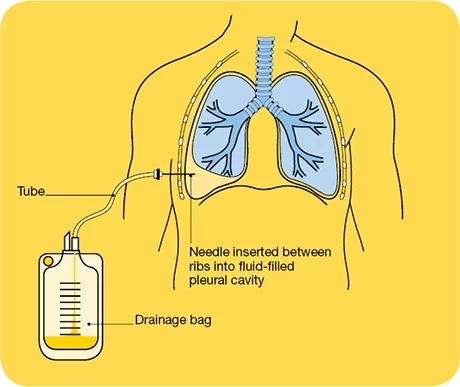
Thoracentesis is performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, specifically to address conditions involving the accumulation of fluid or air in the pleural space, which is the space between the lungs and the chest wall. Here are the main reasons why thoracentesis is performed:
- Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion: Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Thoracentesis is often performed to determine the cause of pleural effusion. Analysis of the fluid can reveal whether the effusion is due to infection, inflammation, heart failure, malignancy, or other underlying conditions.
- Treatment of Symptomatic Pleural Effusion: If pleural effusion is causing symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or respiratory distress, thoracentesis can provide therapeutic relief by draining excess fluid. This helps improve respiratory function and alleviate symptoms.
- Evaluation of Pleural Infections: In cases of suspected pleural infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, thoracentesis allows for the analysis of pleural fluid to identify the causative microorganisms and guide appropriate treatment.
- Management of Pneumothorax: Pneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space, which can cause lung collapse. Thoracentesis may be performed to remove air, helping to re-expand the lung and alleviate symptoms.
- Analysis of Pleural Fluid for Cancer Cells: In individuals with suspected pleural malignancies, thoracentesis can provide a sample of pleural fluid for cytological examination. The presence of cancer cells in the fluid may indicate the spread of cancer to the pleura.
- Relief of Respiratory Symptoms in Heart Failure: In some cases of congestive heart failure, fluid may accumulate in the pleural space. Thoracentesis can be used to drain this fluid, reducing respiratory symptoms associated with heart failure.
- Assessment of Transudative vs. Exudative Effusions: Thoracentesis helps differentiate between transudative and exudative effusions. This classification assists in determining the underlying cause of the effusion, with transudative effusions often related to systemic conditions like heart or liver failure, and exudative effusions linked to inflammation, infection, or malignancy.
- Preoperative Evaluation: Prior to certain surgeries, particularly chest surgeries, thoracentesis may be performed to reduce the risk of complications related to pleural effusion during the procedure.
Thoracentesis is a valuable medical procedure that plays a crucial role in both diagnosing the underlying causes of pleural abnormalities and providing therapeutic relief for individuals experiencing symptoms related to pleural effusion or pneumothorax. The decision to perform thoracentesis is based on the patient’s clinical presentation, medical history, and imaging findings.
Invest in your lung health with Dr. Parthiv Shah, the Best pulmonologist in Mumbai. Discover superior pulmonary care and take control of your well-being. Contact us now!