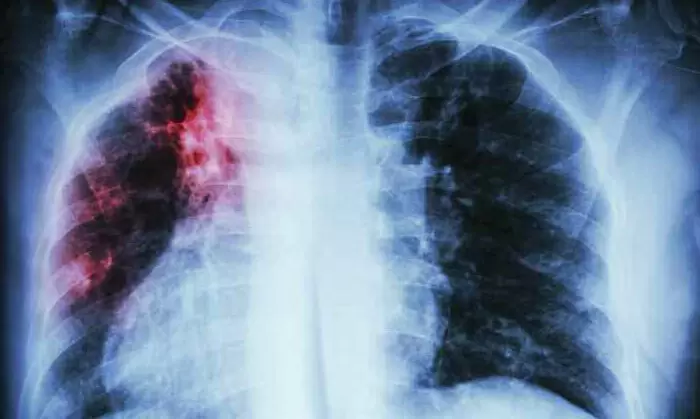
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) can have various causes, and it often results from damage to the lung tissue, leading to inflammation and scarring. Some common causes and risk factors for ILD include:
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): IPF is a specific and often progressive form of ILD where the cause is unknown. It primarily affects the interstitium, leading to the formation of scar tissue.
- Environmental and Occupational Exposures: Prolonged exposure to certain environmental and occupational hazards, such as asbestos, silica dust, coal dust, and other toxic substances, can contribute to ILD.
- Connective Tissue Diseases: Some autoimmune or connective tissue diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis (scleroderma), and lupus, can be associated with ILD.
- Drug-Induced ILD: Certain medications, particularly some chemotherapy drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotics, can cause ILD as a side effect.
- Infections: Some infections, such as viral or fungal infections, can lead to inflammation in the lungs and contribute to ILD.
- Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: This condition is caused by repeated exposure to specific allergens or irritants, often in occupational or environmental settings.
- Sarcoidosis: Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that can affect multiple organs, including the lungs. It may result in granulomas (small inflammatory nodules) in the lung tissue.
- Genetic Factors: In rare cases, genetic factors may predispose individuals to ILD. Some forms of ILD can run in families.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy for cancer, especially when directed at the chest, can cause inflammation and scarring in the lungs.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic aspiration of stomach contents due to GERD may contribute to ILD in some cases.
It’s important to note that in many cases, the cause of ILD may not be clearly identified, leading to the term “idiopathic” (meaning of unknown cause). The exact mechanisms by which these factors lead to ILD are complex and can involve a combination of inflammation, immune system dysfunction, and the activation of fibrotic pathways.
If someone is experiencing symptoms of ILD, such as persistent cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue, or if there are concerns about lung health, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional, typically a pulmonologist, can conduct a thorough evaluation, including imaging studies and pulmonary function tests, to diagnose the specific type of ILD and determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Elevate your respiratory health with the expertise of Dr. Parthiv Shah, recognized as the Best Pulmonologist in Mumbai. As a board-certified specialist, Dr. Shah brings a wealth of experience and a patient-centric approach to comprehensive pulmonary care.