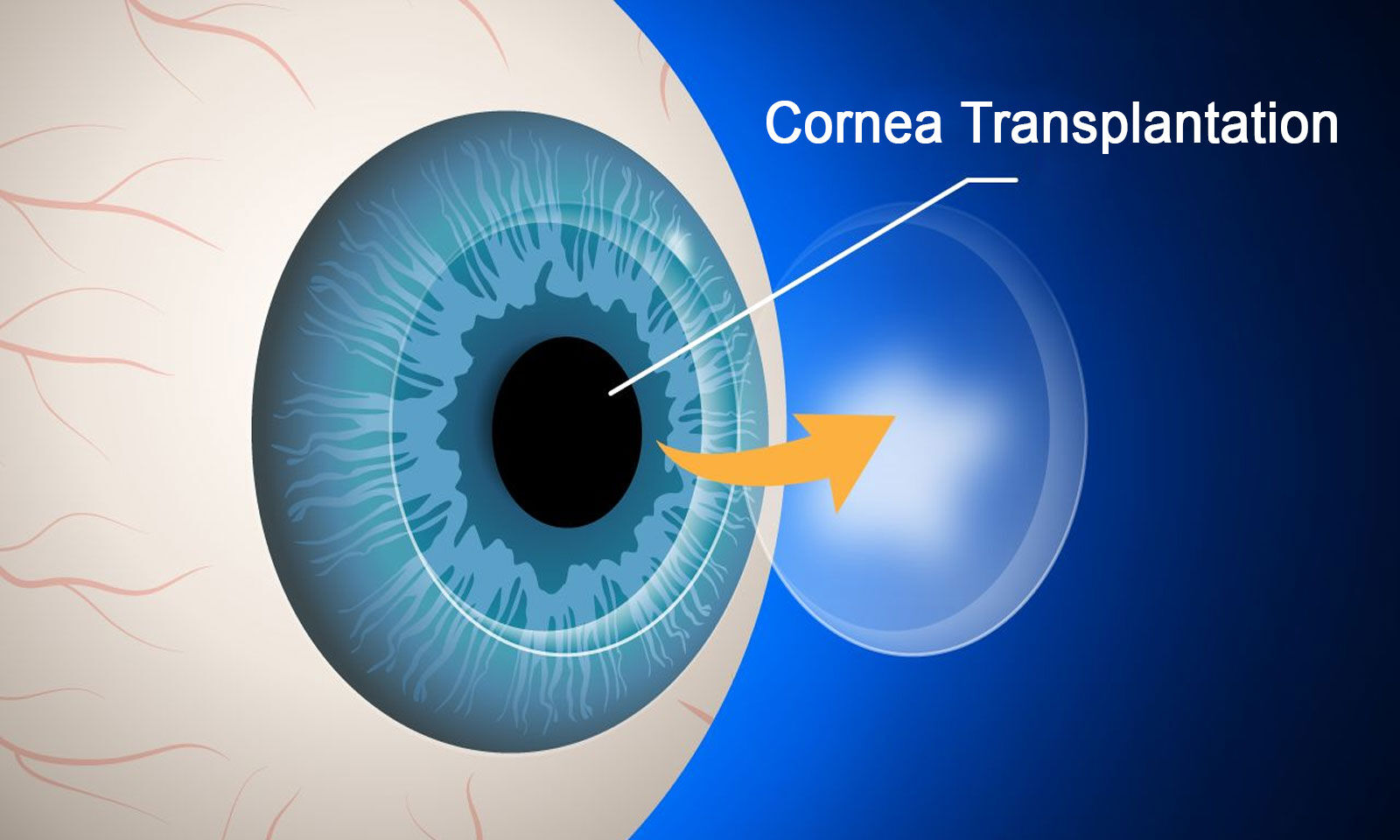
A corneal transplant, also known as a corneal graft, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea. The cornea is the clear, transparent front surface of the eye, and it plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, which is essential for vision. When the cornea is damaged or diseased to the extent that it cannot perform its optical function adequately, a corneal transplant may be necessary.
Here are some key points about corneal transplants and when they are necessary:
1. Indications for Corneal Transplant:
– Corneal transplants are typically performed when the cornea is damaged or affected by conditions that cannot be effectively treated through other means. Common reasons for corneal transplants include:
– Keratoconus: A progressive thinning and bulging of the cornea that distorts vision.
– Fuchs’ Dystrophy: A genetic disorder that causes swelling and clouding of the cornea.
– Corneal Scarring: Resulting from injuries, infections (e.g., herpes keratitis), or previous surgeries.
– Corneal Transplant Rejection: In cases where the body’s immune system rejects a previous corneal transplant.
– Thinning of the Cornea: Due to conditions like keratoconus or certain corneal degenerations.
– Corneal Degenerations: Conditions that cause structural changes in the cornea, impacting vision.
– Corneal Ulcers: Severe corneal infections that may lead to scarring.
2. Types of Corneal Transplants:
– There are different types of corneal transplant procedures, including:
– Penetrating Keratoplasty (PKP): In PKP, the entire central cornea is replaced with a donor cornea.
– Endothelial Keratoplasty (EK): EK procedures replace only the innermost layer of the cornea, where conditions like Fuchs’ dystrophy primarily affect.
– Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (DALK): DALK replaces the front and middle layers of the cornea, leaving the endothelium intact.
3. The Donor Cornea:
– Donor corneas are obtained from individuals who have donated their corneas after death. Eye banks carefully screen and store donated corneas for transplantation. The tissue is rigorously tested for infectious diseases to ensure safety.
4. Recovery and Healing:
– After a corneal transplant, patients typically experience some discomfort and require time for the eye to heal. Vision improvement can be gradual, and it may take several months to achieve the best visual outcome. Medications to prevent infection and rejection are prescribed during the recovery period.
5. Success Rates:
– Corneal transplants have a high success rate, with most patients experiencing improved vision and a better quality of life. However, the outcome can vary depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated.
6. Follow-Up Care:
– Regular follow-up visits with an ophthalmologist are crucial after a corneal transplant to monitor the graft’s health, adjust medications as needed, and address any potential complications.
Corneal transplants are essential procedures that can significantly improve vision and alleviate discomfort for individuals with severe corneal conditions. The decision to undergo a corneal transplant is made based on a thorough evaluation by an eye care specialist, taking into account the individual’s specific eye condition and needs.
It’s important to consult Dr. Vaidya one of the Best Cornea Specialist in Mumbai know more information visit our hospital at Dr. Vaidya Eye Hospital.