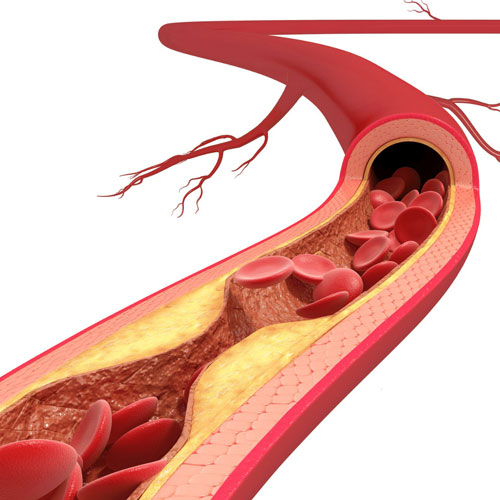
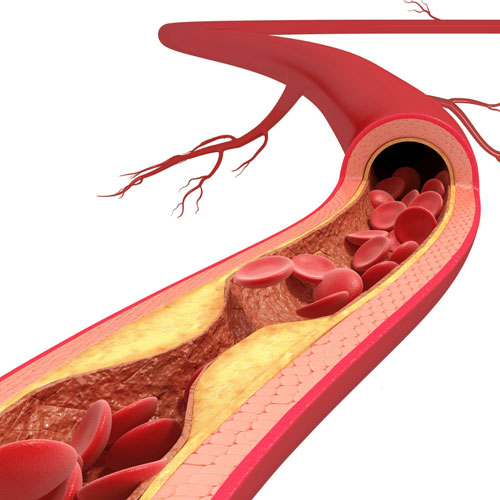
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD), also known as Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a progressive and systemic disease that results in the narrowing and hardening of arteries throughout the body. Atherosclerosis occurs due to the accumulation of fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances within the arterial walls. These deposits, often referred to as plaque, can lead to the following processes and complications:
1-Plaque Formation: Over time, plaque builds up in the arteries, causing them to become narrow and stiff.
2-Reduced Blood Flow: The narrowing of the arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the affected areas, typically the limbs (most commonly the legs).
3-Inflammation and Blood Clots: Plaque can cause inflammation in the arterial walls, leading to the formation of blood clots. These clots can further block blood flow or break off and travel to smaller vessels, causing sudden blockages.
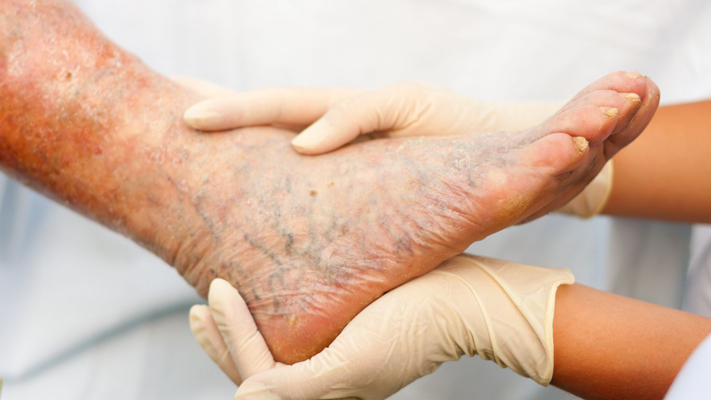
4-Tissue Damage: Insufficient blood supply can result in tissue damage, leading to symptoms such as leg pain, cramping, numbness, and weakness, especially during physical activity.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and PVD, including:
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of vascular disease
- Aging
- Certain medical conditions
It’s important to note that while atherosclerosis is the primary cause of PVD, other conditions like arterial inflammation or injury can also contribute to vascular problems. Managing and addressing risk factors, as well as adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, are essential in preventing and managing PVD.
For more information, consult Dr. Kunal Arora One of the Best Interventional Radiologist in Mumbai or you can contact us on 9004093053.