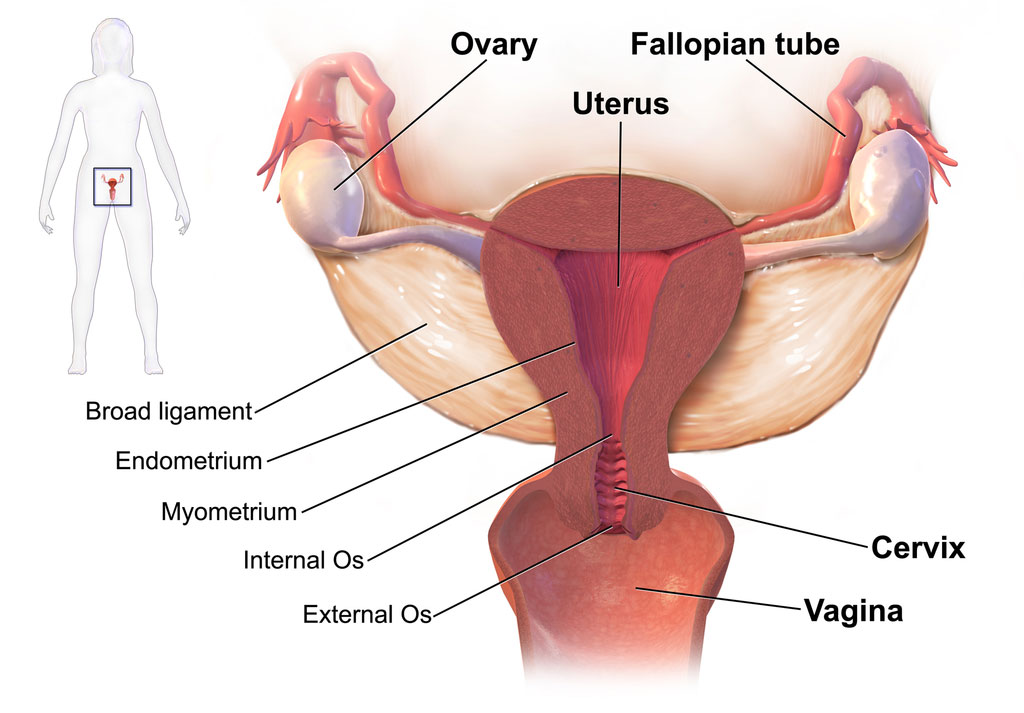
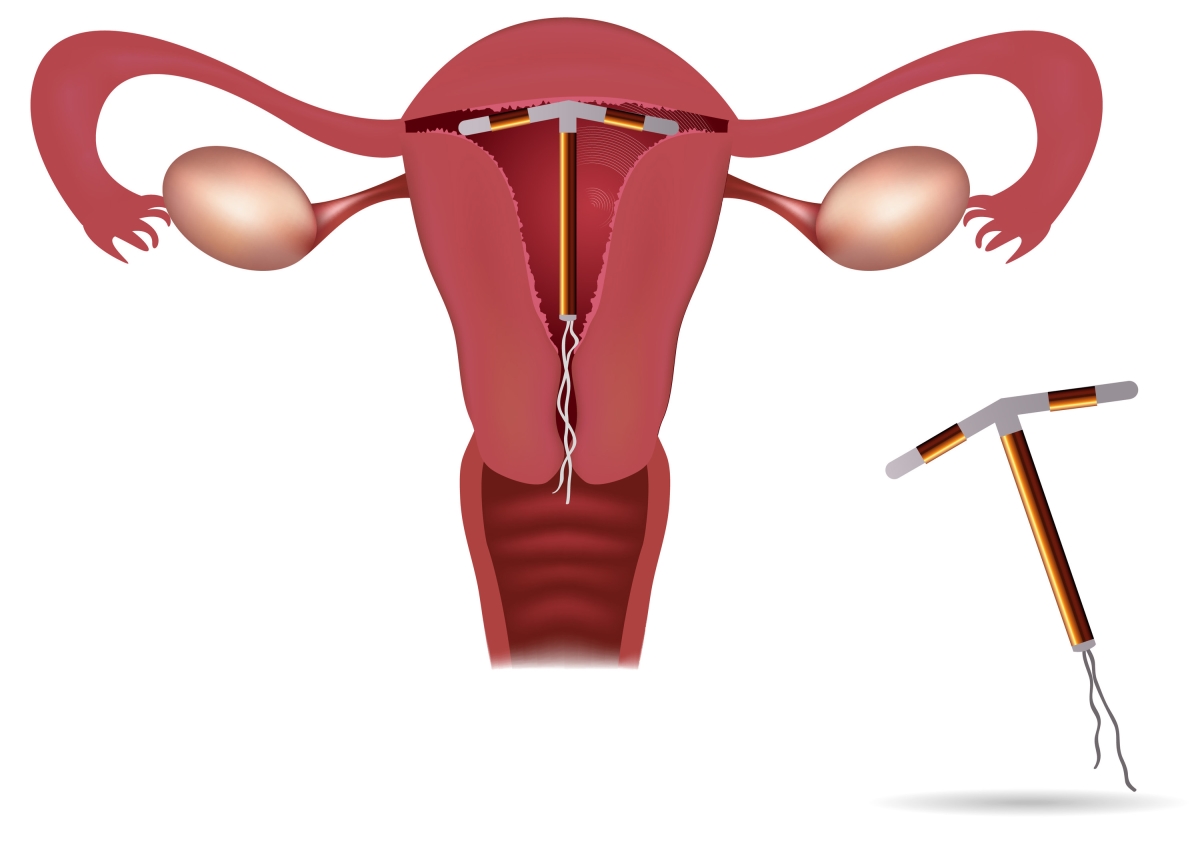
Tube cannulation is a medical procedure that involves the insertion of a tube or catheter into a vessel, duct, or body cavity for a variety of therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. This procedure is commonly used in healthcare settings to provide access to specific areas of the body for the following reasons:
- Medication Administration: One of the most common uses of tube cannulation is to administer medications directly into the bloodstream. For example, central venous catheters (CVCs) are often used to deliver intravenous (IV) medications, such as antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, or nutrition solutions, directly into a large central vein.
- Fluid or Blood Collection: Tubes can be used to collect samples of blood, urine, or other bodily fluids for diagnostic testing. This is commonly done through catheters or tubes that are placed in the urinary tract, blood vessels, or the gastrointestinal tract.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Some patients may require tube feeding due to difficulty swallowing, gastrointestinal problems, or the need for specialized nutrition. Gastrostomy or jejunotomy tubes are examples of tubes used for this purpose.
- Fluid or Gas Drainage: Certain medical conditions, such as pleural effusions or abdominal abscesses, may require the removal of excess fluid or gas. Chest tubes and abdominal drainage tubes can be inserted for this purpose.
- Monitoring: Tube cannulation can be used for monitoring purposes, such as measuring central venous pressure (CVP) through a CVC or monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) with an intraventricular catheter.
The choice of tube and its placement location depend on the patient’s medical needs, the type of therapy or treatment required, and the assessment of the healthcare provider. For example:
- Central Venous Catheters (CVCs) are typically inserted in large veins near the heart, often in the neck, chest, or groin.
- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters (PICCs) are usually placed in a peripheral vein, often in the arm, and threaded through to a larger vein closer to the heart.
- Urinary Catheters are inserted into the bladder through the urethra or, in certain cases, directly through the abdominal wall (suprapubic catheter).
It’s important to note that tube cannulation should be performed by trained healthcare professionals to ensure the safety and well-being of the patient. The procedure may require local anesthesia or sedation, and it should be carried out with aseptic techniques to minimize the risk of infection.
The duration of tube placement can vary, and tubes are typically removed when they are no longer needed, when complications arise, or as determined by the treating medical team. Proper care, monitoring, and maintenance of the tube are essential to prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcome for the patient.
Ready to prioritize your women’s health? Schedule your appointment with Dr. Neha, your trusted Gynaecologist in Dubai today!