Several factors can contribute to the classification of a pregnancy as high-risk. Common risk factors include:
Advanced Maternal Age: Pregnancy in women over the age of 35 is considered advanced maternal age. Older mothers may face an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., Down syndrome) and other complications.
Teenage Pregnancy: Pregnancies in adolescents (usually under 18) are considered high-risk due to the increased likelihood of complications such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
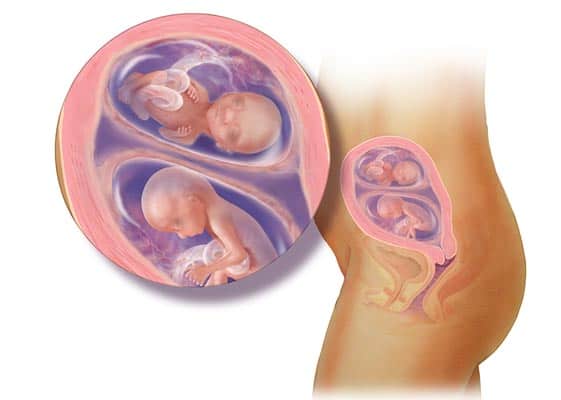
Multiple Pregnancies: Carrying twins, triplets, or more increases the risk of complications, including preterm birth, low birth weight, and gestational diabetes.
Pre-existing Health Conditions: Diabetes: Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can increase the risk of birth defects and complications.
Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can lead to preeclampsia and other complications.
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis may increase the risk of complications.
History of Pregnancy Complications: Women with a history of preterm birth, preeclampsia, or other complications in previous pregnancies may be at a higher risk in subsequent pregnancies.
Genetic Factors: Certain genetic conditions or a family history of genetic disorders can increase the risk of birth defects and complications.
Infections: Certain infections, such as cytomegalovirus (CMV) or rubella, can pose risks to both the mother and the developing fetus.
Body Mass Index (BMI): Both underweight and overweight conditions can contribute to complications during pregnancy. Obesity increases the risk of gestational diabetes, hypertension, and other issues.
Substance Use: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and illicit drug use during pregnancy can lead to various complications, including preterm birth, low birth weight, and developmental issues.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Women who conceive through fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may have a higher risk of certain complications.
Certain Ethnic Backgrounds: Some ethnic groups may be at a higher risk for specific pregnancy complications. It’s important to consider individual and family medical histories.
Uterine and Placental Conditions: Conditions such as uterine fibroids or placenta previa can increase the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Factors: Poor nutrition, inadequate prenatal care, and high levels of stress can contribute to an increased risk of complications during pregnancy.
It’s crucial for healthcare providers to assess these factors early in pregnancy to identify potential risks and develop appropriate management plans. Regular prenatal care and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for addressing and mitigating these risk factors.
Are you looking for top-notch women’s healthcare in Mira Road? Your search ends here with Dr. Deepika Doshi, a highly experienced and caring Gynecologist in Mira Road dedicated to your well-being.