Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair in Bangalore is a modern, minimally invasive solution for patients suffering from shoulder pain, weakness, and limited mobility due to rotator cuff tears, helping them return to daily activities and sports with confidence and less downtime. This advanced procedure is performed using an arthroscope through tiny incisions, leading to precise tendon repair, reduced scarring, and quicker rehabilitation compared to traditional open surgery.
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair in Bangalore
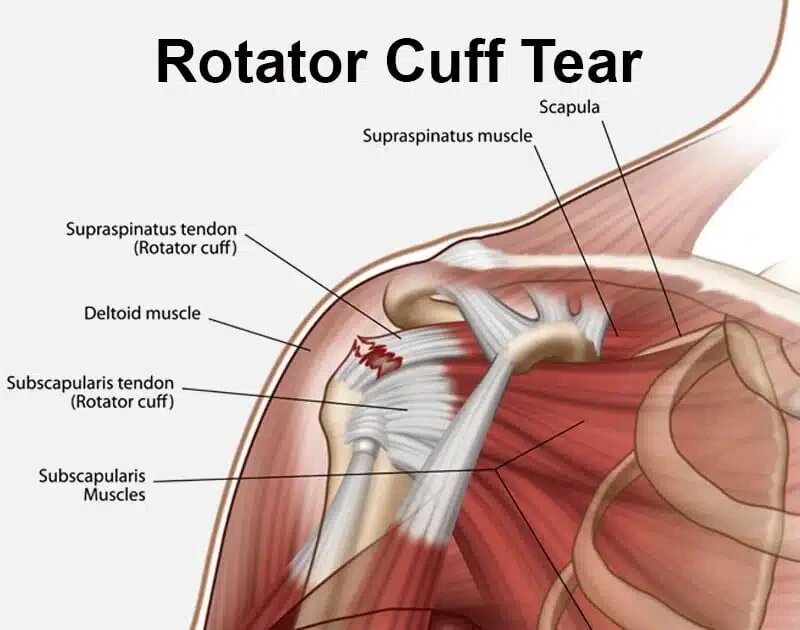
Rotator cuff tears are common in athletes and older adults, often presenting with night pain, weakness while lifting or rotating the arm, and restricted shoulder movement. Arthroscopic repair is typically recommended when conservative treatments such as rest, medications, and physiotherapy fail, or in cases of large, high-grade partial or full-thickness tears—especially with tendon retraction of ≥1cm. The procedure is also ideal for active individuals and athletes who wish to return to sports efficiently with the support of minimally invasive techniques.
How the procedure works
During arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, a small camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the shoulder joint through keyhole incisions, providing a clear view of the torn tendon while specialized instruments are used to repair and reattach it to the bone. This technique minimizes tissue damage and allows targeted, accurate repair, often resulting in less pain and a smoother recovery journey.
Who is a good candidate?
Surgery is generally advised for those with:
- Persistent symptoms for 6–12 months with significant pain and functional loss.
- Full-thickness tears, large retracted tears, or high-grade partial tears (>60%) not responding to conservative management.
- Weakness that affects work, sports, or daily living, or for athletes aiming for timely return to play.
Symptoms that suggest a rotator cuff tear
Common signs include:
- Pain at rest and during the night, especially while lying on the affected shoulder.
- Pain or weakness during lifting or rotational movements.
- Popping/clicking and reduced range of motion in the shoulder.
Surgical options explained
- Traditional Open Repair: Involves a larger incision and deltoid splitting for access, typically reserved for large, complex tears or when additional reconstruction (e.g., tendon transfers) is needed; recovery is generally longer.
- All-Arthroscopic Repair: Performed entirely through small portals using a camera and mini instruments; ideal for most tears with outpatient recovery, minimal scarring, and quicker rehabilitation.
- Mini-Open Repair: Combines arthroscopy to address joint issues (like bone spurs) with a smaller open incision to complete the repair, offering a balance between direct visualization and less invasiveness.
Benefits of arthroscopic repair
- Minimally invasive with smaller incisions and less tissue disruption.
- Faster recovery and reduced postoperative pain compared to open surgery.
- Improved shoulder function with restoration of strength and mobility.
- Lower risk of infection due to smaller incisions.
Risks and considerations
While generally safe, possible complications include infection, bleeding, stiffness, nerve injury, re-tear of the tendon, and anesthesia-related events; careful postoperative care and physiotherapy help minimize these risks.
Recovery timeline and rehabilitation
- Initial Healing: The arm is immobilized in a sling for the first few weeks to protect the repair while pain is managed with medications.
- Physiotherapy: Rehab starts with passive range of motion, progressing to active motion and then strengthening, typically phased over several weeks to months.
- Return to Activities: Many resume normal activities around 4–6 months, while complete recovery and full sports participation can take 6–12 months depending on tear size, tissue quality, and adherence to rehab.
Rehabilitation phases
- Phase 1: Passive range of motion to prevent stiffness.
- Phase 2: Active range of motion to restore movement patterns.
- Phase 3: Strengthening to rebuild rotator cuff and scapular muscles.
- Phase 4: Advanced strengthening and functional training for return to work/sport.
Preparing for surgery
A thorough evaluation with medical history, physical exam, and imaging helps plan the repair, along with preoperative instructions on fasting and medications, and a clear postoperative plan for sling use, wound care, and physiotherapy.
What to expect after surgery
Post-surgery, patients receive pain control, shoulder immobilization with a sling, and detailed discharge instructions covering wound care, medications, sleeping positions, and activity restrictions. Any unusual pain, swelling, redness, or concerns should be reported promptly, and all follow-up visits and therapy sessions should be maintained.
Contact Us
For expert Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair in Bangalore, consult Dr. Ponnanna K.M.
- Dr. Ponnanna K.M – Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
- Opera Bone and Joint Clinic, #14, Ground Floor, 4th Main, 6th Cross, Malleswaram, Bangalore – 560003
- Call: 89515 45276
- Email: dr.ponnanna@gmail.com
Reach out to book an appointment or send a query through the official Contact page.
