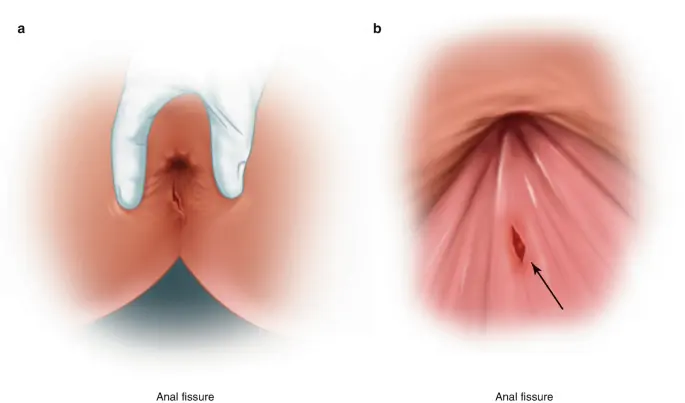
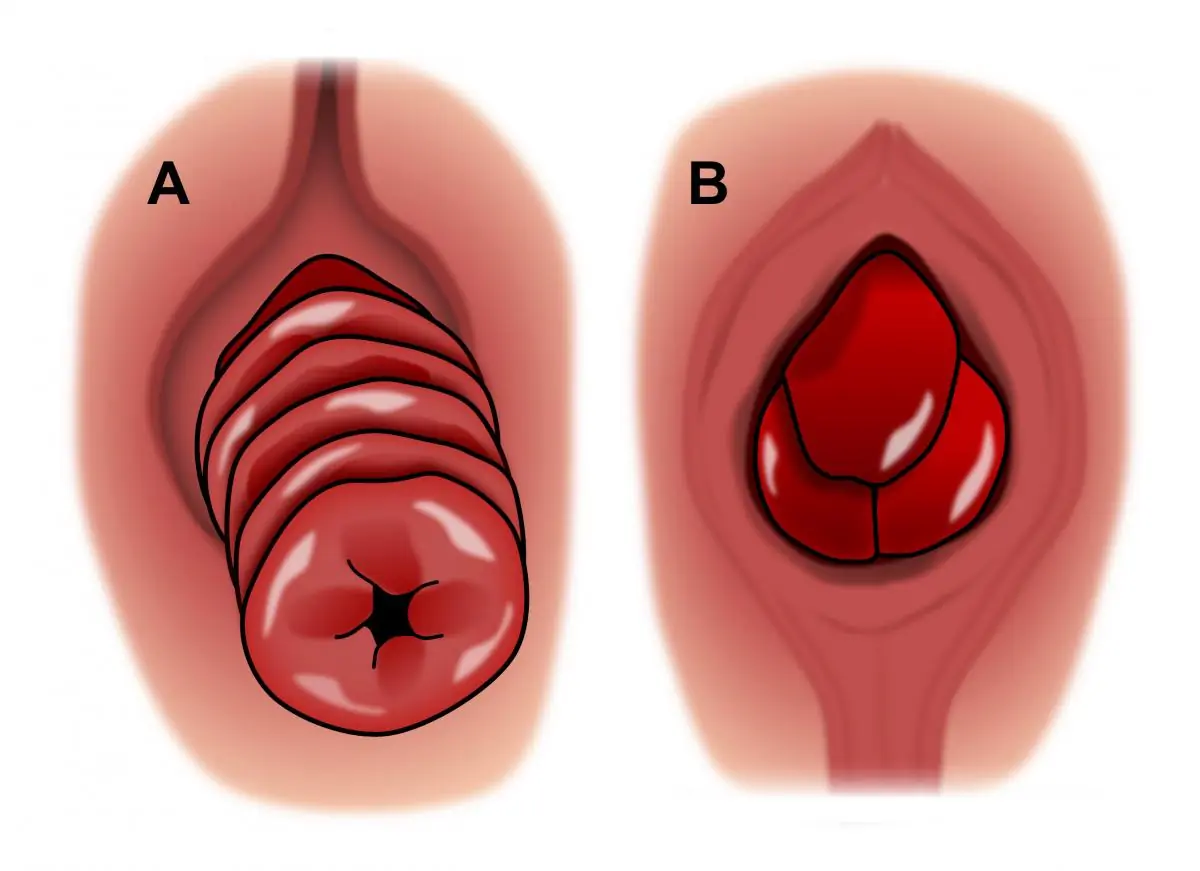
Anal fissures are typically caused by factors that lead to the tearing or damage of the sensitive skin lining the anus. Common causes of anal fissures include:
- Straining during Bowel Movements: Putting excessive pressure on the anal canal when passing hard or large stools can cause fissures.
- Constipation: Chronic constipation can lead to the passage of hard stools, which can irritate and tear the anal lining.
- Diarrhea: Frequent episodes of diarrhea can weaken the anal skin, making it more susceptible to fissures.
- Childbirth: Anal fissures can occur during childbirth, particularly if there is tearing or trauma during delivery.
- Anal Trauma: Physical injury or trauma to the anal area, such as from the insertion of foreign objects, can lead to fissures.
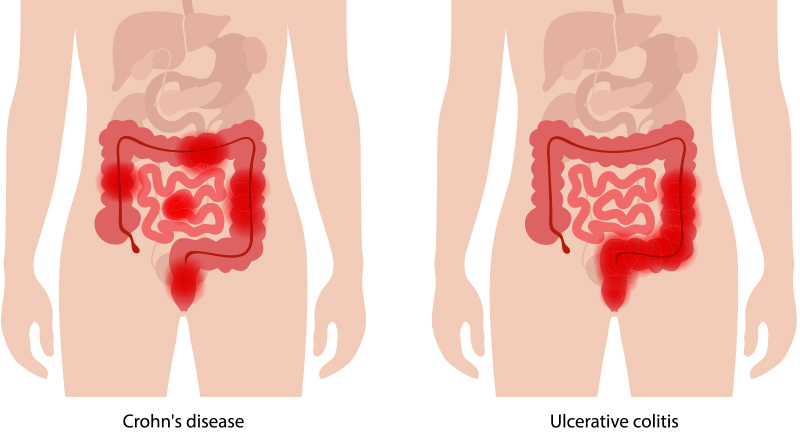
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, which involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, can increase the risk of anal fissures.
- Reduced Blood Flow: Certain medical conditions that reduce blood flow to the anal area, such as Raynaud’s disease, can contribute to fissures.
- Anal Sphincter Muscle Spasms: Persistent contractions or spasms of the anal sphincter muscles can hinder the healing of existing fissures or lead to new ones.
Addressing the underlying causes and risk factors is essential to prevent the development or recurrence of anal fissures. This may involve lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical treatment to manage conditions like constipation or diarrhea. If you suspect you have an anal fissure or are experiencing symptoms, it’s advisable to seek medical evaluation and guidance for appropriate treatment and prevention.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with Anal fissures disease, consult Dr. Chintamani Godbole one of the best Gastrointestinal Doctor in Mumbai.