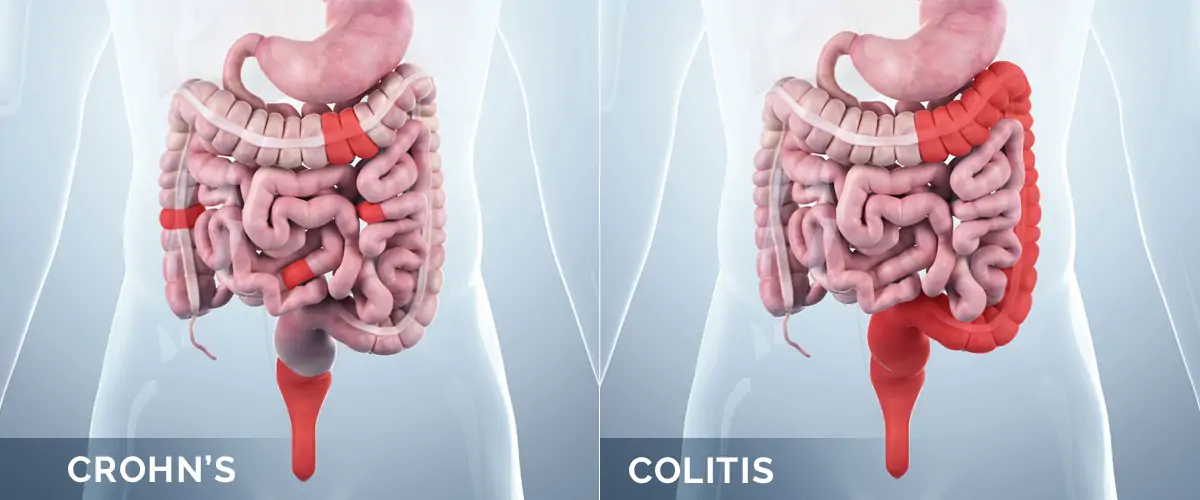
Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease are both forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but they have some key differences. Here are the primary distinctions between the two conditions:
1-Location of Inflammation:
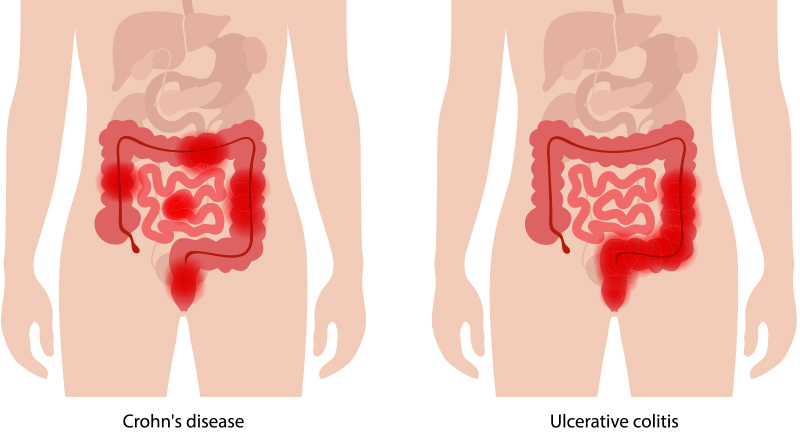
- Ulcerative Colitis: Inflammation occurs only in the inner lining of the colon (large intestine) and rectum. It typically begins in the rectum and may extend to other parts of the colon in a continuous fashion.
- Crohn’s Disease: Inflammation can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. It can involve segments of the small intestine, large intestine, or both, and the inflammation is not continuous but can appear in patches with healthy tissue in between.
2-Depth of Inflammation:
- Ulcerative Colitis: Inflammation is confined to the innermost lining (mucosa) of the colon and rectum.
- Crohn’s Disease: Inflammation can extend through the entire thickness of the intestinal wall, involving all layers, including the mucosa, submucosa, and even deeper layers.
3-Pattern of Inflammation:
- Ulcerative Colitis: Inflammation typically forms continuous areas of ulceration and irritation, often leading to symptoms like bloody diarrhea and frequent bowel movements.
- Crohn’s Disease: Inflammation creates a patchy or skip pattern, where areas of diseased tissue are interspersed with healthy tissue. This can result in a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and complications like strictures or fistulas.
4-Complications:
- Ulcerative Colitis: Complications primarily involve issues related to the colon and rectum, such as severe bleeding, toxic megacolon, and an increased risk of colon cancer.
- Crohn’s Disease: Complications can affect any part of the digestive tract and may involve strictures (narrowing of the intestine), fistulas (abnormal connections between tissues), and abscesses. Crohn’s patients may also have complications in other areas, such as the skin, eyes, and joints.
5-Surgical Treatment:
- Ulcerative Colitis: Surgical treatment often involves removing the entire colon and rectum (total colectomy) with the creation of an ileostomy or an ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA).
- Crohn’s Disease: Surgery typically aims to remove diseased sections of the intestine, but it can be challenging because of the skip pattern of inflammation. Repeat surgeries may be necessary in Crohn’s patients.
It’s essential to consult with a gastroenterologist or healthcare provider for a precise diagnosis and tailored treatment plan, as the distinction between Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease is crucial in determining the most appropriate management approach.
Looking for expert Colorectal Surgeon in Mumbai ? Dr. Chintamani Godbole offers specialized treatment for colorectal conditions or you can contact us on 8451865944.