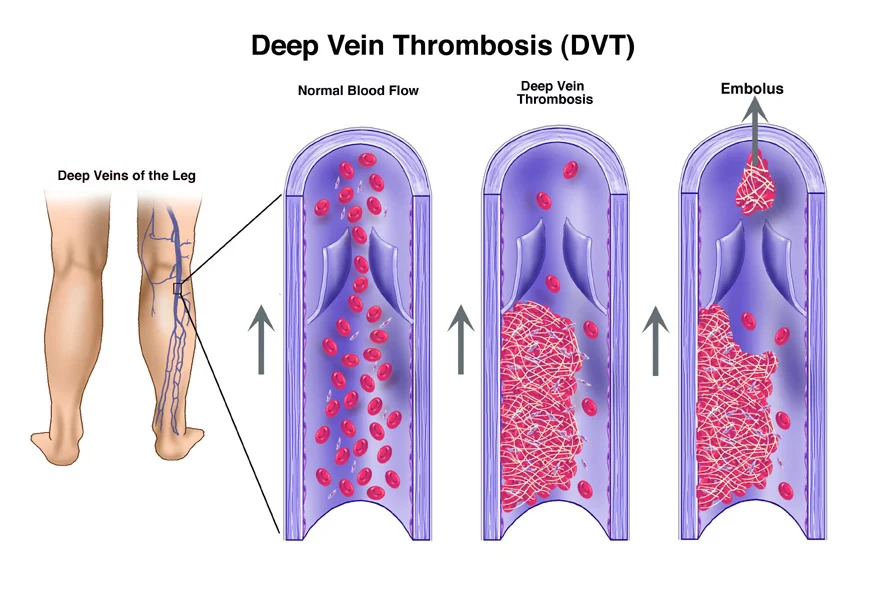
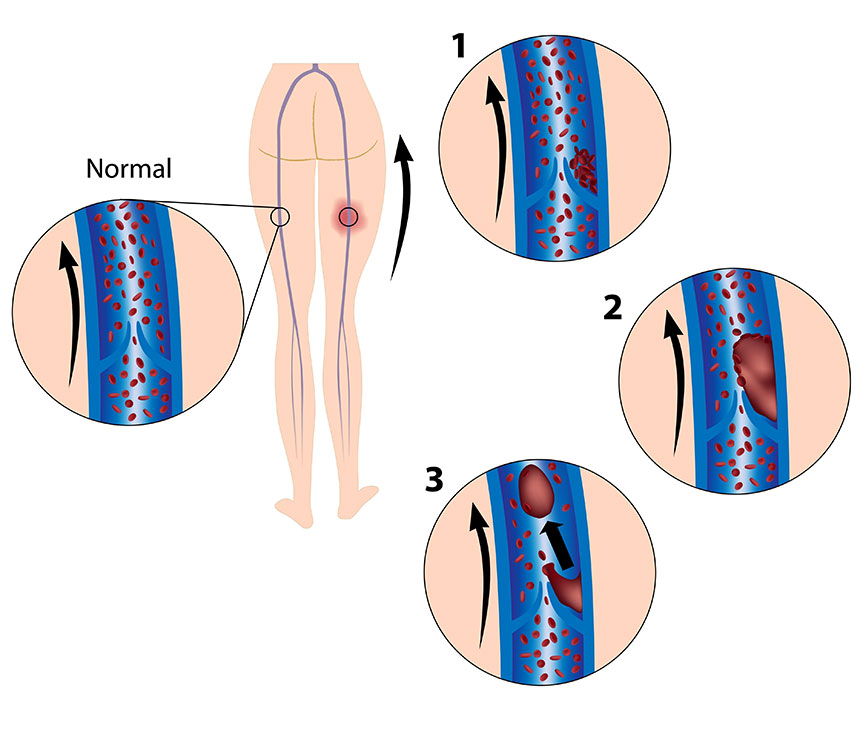
Yes, there are risks associated with interventional Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) treatment. While these procedures are generally considered safe and effective, it’s important to be aware of potential complications. Some of the risks associated with interventional DVT treatment include:
- Bleeding: The insertion of catheters or other instruments may cause bleeding at the site of entry. Severe bleeding is a rare but possible complication.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the site where catheters are inserted or in the treated blood vessels.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may have allergic reactions to medications used during the procedure.
- Blood Clots: In rare cases, the procedure itself could dislodge clots, leading to embolism or blockages in other blood vessels.
- Vascular Injury: The blood vessels being treated may be damaged during the procedure, although this is uncommon.
- Re-stenosis or Re-occlusion: There is a risk that the treated blood vessels may narrow again or become blocked after the procedure.
- Pulmonary Embolism: In some cases, the dislodgment of clots during treatment could lead to a pulmonary embolism, where clots travel to the lungs.
It’s crucial for individuals considering interventional DVT treatment to have a thorough discussion with their interventional radiologist. The healthcare provider will assess the individual’s overall health, medical history, and the specific characteristics of the DVT to determine the most appropriate course of action. The potential risks and benefits of the procedure will be discussed in detail, allowing the patient to make an informed decision about their treatment.
Ready to experience top-notch care in interventional radiology? Consult with Dr. Kunal Arora, recognized as the top Interventional Radiologist in Mumbai. Schedule your appointment now for expert guidance and advanced interventions. 📞9004093053