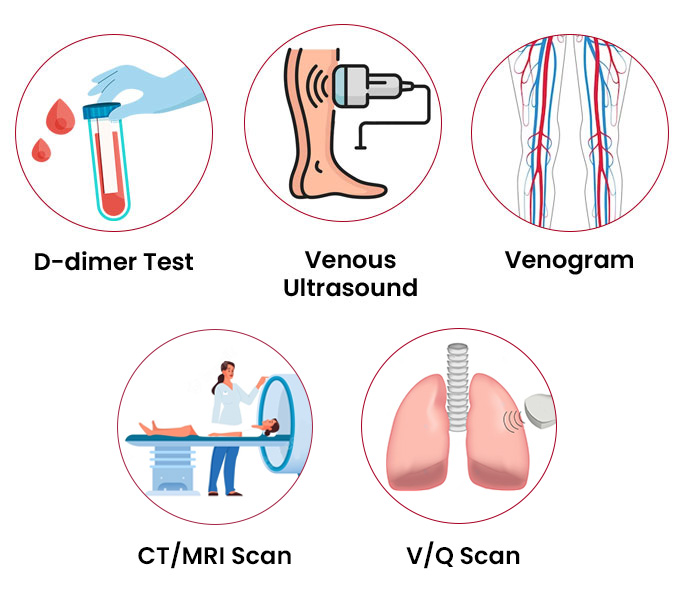
Diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) typically involves a combination of clinical assessment, medical history review, and various diagnostic tests. Here is an overview of the diagnostic process for DVT:
1- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Discussion of symptoms, medical history, and risk factors for DVT.
- Physical examination to check for signs such as swelling, tenderness, or discoloration in the affected area.
2- Ultrasound Imaging:
- Widely used technique to diagnose DVT.
- Uses sound waves to create images of veins and assess blood flow.
- Doppler ultrasound helps visualize blood flow and detect blood clots.
3- D-Dimer Test:
- Blood test measuring the presence of a substance produced during blood clot dissolution.
- Elevated D-dimer levels may indicate a blood clot, used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods.
4- Venography:
- Involves injecting contrast dye into veins and taking X-ray images.
- Visualizes veins and identifies potential blockages caused by blood clots.
5- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- Used in specific cases to obtain detailed images of veins and identify blood clots.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism:
1- CT Venography:
- Creates 3D images to detect pulmonary embolism within lung arteries.
- Outlines pulmonary arteries using contrast.
2- Pulmonary Angiography:
- Provides a clear picture of blood flow in lung arteries.
- Considered the most accurate method for diagnosing pulmonary embolism.
3- Ventilation Perfusion Scan:
- Involves injecting a tracer substance into a vein to map blood flow (perfusion) and compare it with airflow to the lungs (ventilation).
For more information, consult Dr. Kunal Arora one of the Best Interventional Radiologist in Mumbai or you can contact us on 9004093053.