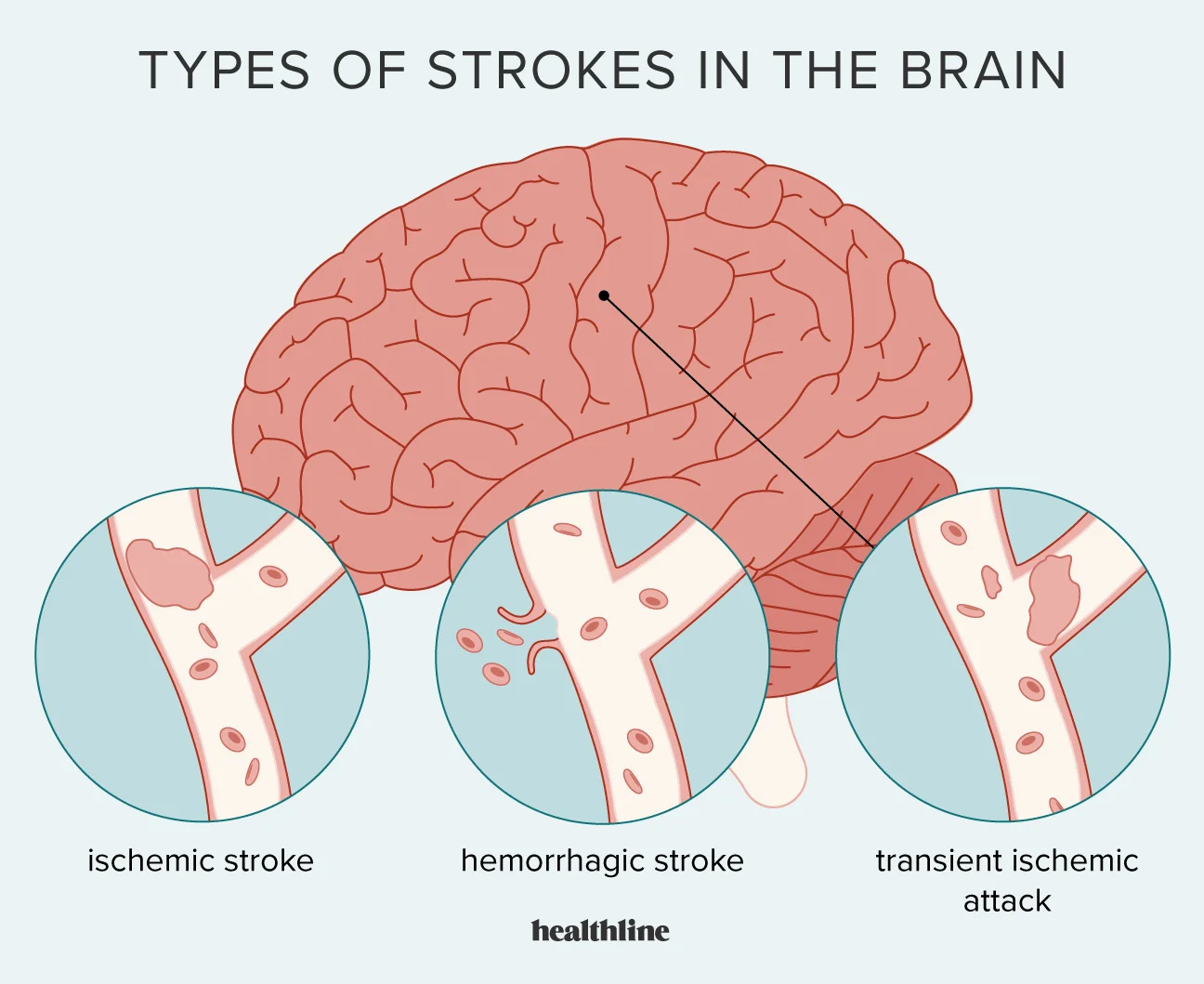
There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. However, there is a third subtype called a transient ischemic attack (TIA), often referred to as a “mini-stroke.” Here’s a breakdown of the three types:
1. Ischemic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a blood clot or plaque buildup blocks an artery, reducing blood flow to a part of the brain. Ischemic strokes are further divided into two subtypes:
– Thrombotic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot (thrombus) that forms within an artery supplying the brain.
– Embolic Stroke: Caused by a clot or debris that forms elsewhere in the body and travels to the brain, blocking a smaller blood vessel.
2. Hemorrhagic Stroke: This type of stroke is characterized by bleeding in the brain due to a ruptured blood vessel. There are two main subtypes of hemorrhagic stroke:
– Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Bleeding occurs within the brain tissue itself.
– Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding happens in the space between the brain and its surrounding membranes.
3. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): A TIA is often referred to as a “mini-stroke.” It is caused by a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain. The symptoms of a TIA are similar to those of a stroke but typically resolve within a short period, usually less than 24 hours. A TIA is considered a warning sign, as it indicates an increased risk of a full-blown stroke in the future.
Each type of stroke has distinct causes, risk factors, and treatment approaches. Prompt medical attention is critical for all types of strokes, as timely intervention can help minimize damage and improve outcomes.
For more information contact, Dr. Amit Shah, a senior consultant Neurologist in Kandivali practicing at Dr. Amit Shah Neurology Clinic.