Heavy menstrual bleeding, medically known as menorrhagia, can be caused by various factors. Some common causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly imbalances in estrogen and progesterone levels, can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle and lead to heavy bleeding.
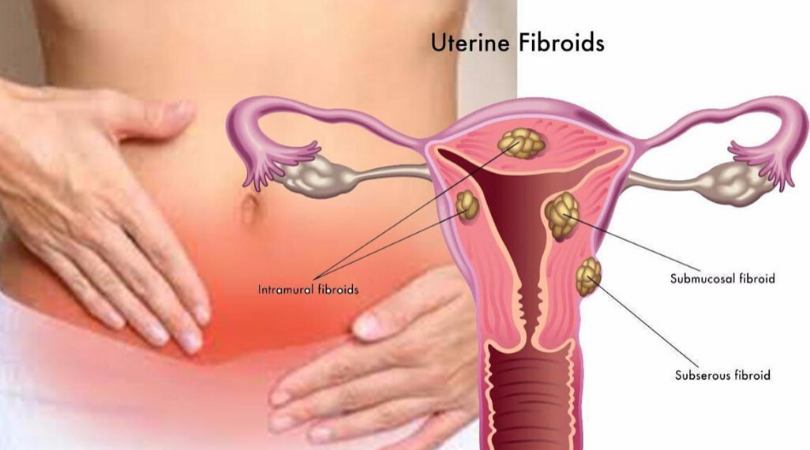
- Uterine Fibroids: Fibroids are noncancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy or prolonged periods.
- Adenomyosis: Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue lining the uterus (endometrium) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, leading to heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Polyps: Uterine polyps are small growths on the inner lining of the uterus that can cause heavy or irregular bleeding.
- Endometrial Hyperplasia: An overgrowth of the uterine lining (endometrium) can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infections in the reproductive organs, such as PID, can cause inflammation and contribute to heavy bleeding.
- Coagulation Disorders: Conditions that affect blood clotting, such as von Willebrand disease or other bleeding disorders, can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding.
- IUD (Intrauterine Device): While hormonal IUDs are sometimes prescribed to reduce menstrual bleeding, copper IUDs may lead to heavier periods in some individuals.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause irregular periods, and in some cases, heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as anticoagulants or anti-inflammatory drugs, may contribute to heavy bleeding.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Though rare, an ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy outside the uterus) can cause heavy bleeding and requires immediate medical attention.
- Thyroid Disorders: Thyroid dysfunction, particularly an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to heavy bleeding.
- Cancer: In rare cases, uterine or cervical cancer may cause heavy menstrual bleeding. It’s important to rule out malignancies, especially in postmenopausal women.
- Intrauterine Synechiae (Asherman’s Syndrome): Scar tissue inside the uterus, often caused by surgery or infection, can lead to adhesions and heavy menstrual bleeding.
If someone is experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis. Treatment options will depend on the underlying cause and may include medications, hormonal therapies, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery, depending on the severity and specific condition.
Take the first step towards reproductive health and well-being with Dr. Deepika Doshi, your trusted Gynecologist in Mira Road.