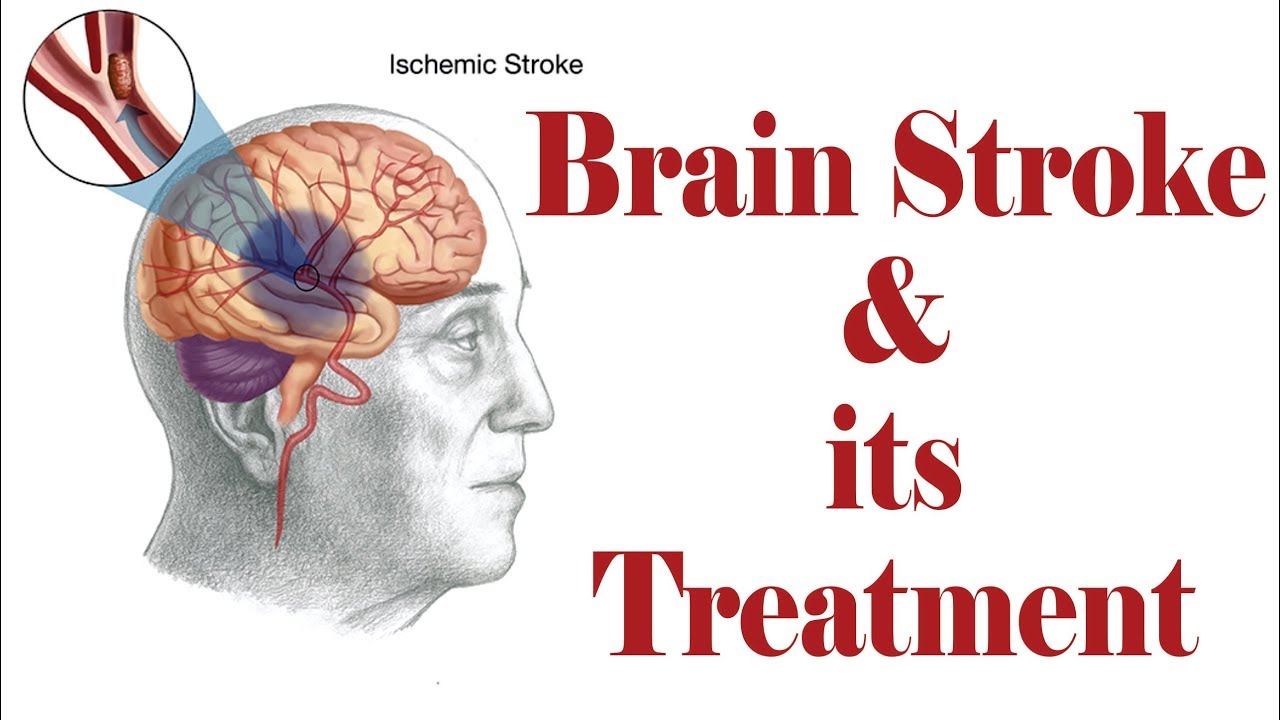
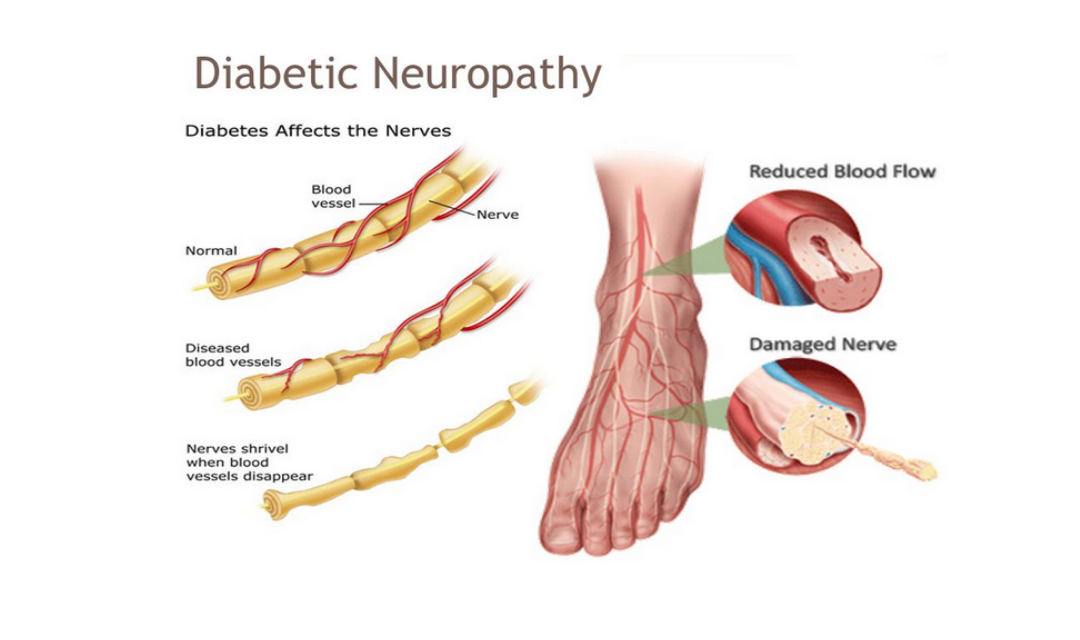
Migraines can be triggered by a variety of factors, and these triggers can vary among individuals. Identifying and avoiding your specific triggers can help in migraine management. Common migraine triggers include:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly in women, can trigger migraines. Hormonal changes related to the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause, or the use of birth control pills can be significant triggers.
- Stress: Emotional stress, anxiety, and tension are frequent triggers for migraines. Relaxation techniques and stress management may help reduce the impact of stress-related migraines.
- Dietary Factors: Certain foods and drinks are known to trigger migraines in some people. Common dietary triggers include alcohol (especially red wine), caffeine, aged cheeses, chocolate, processed meats, and foods containing the flavor enhancer MSG (monosodium glutamate).
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water or becoming dehydrated can provoke migraines. Staying well-hydrated is essential in migraine prevention.
- Skipped Meals: Missing meals or going too long without eating can lead to low blood sugar levels, which may trigger a migraine.
- Sleep Patterns: Changes in sleep patterns, such as getting too much or too little sleep, can be a trigger. Establishing a regular sleep schedule is important for migraine management.
- Environmental Factors: Sensory stimuli can trigger migraines in some individuals. Bright or flickering lights, loud noises, strong odors, and changes in weather or barometric pressure are common environmental triggers.
- Physical Exertion: Intense physical activity or exertion can lead to “exercise-induced” migraines in some people.
- Medications: Certain medications, including vasodilators and hormonal medications, can trigger migraines as a side effect.
- Alcohol and Caffeine: While alcohol and caffeine can be migraine triggers for some individuals, sudden caffeine withdrawal can also lead to headaches or migraines.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly in women, can trigger migraines. Hormonal changes related to the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause, or the use of birth control pills can be significant triggers.
- Stimulants and Artificial Sweeteners: Some people report that stimulants like aspartame (an artificial sweetener) and certain food additives can trigger migraines.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with migraines have the same triggers, and some may not identify any specific triggers at all. Keeping a migraine diary to track potential triggers and headache patterns can be helpful in identifying and managing individual triggers.
If you experience frequent or severe migraines, consulting a healthcare provider or a headache specialist can help develop a personalized management plan that may include lifestyle changes and, if needed, medications to prevent or treat migraines.
Unlock relief and expert care with Dr. Amit Shah, your trusted Neurologist in Mumbai. Take the first step toward better brain health and schedule your consultation today.”