During a gynecological exam, you can expect a series of steps and procedures designed to assess and maintain your reproductive health. While the exact details may vary based on your age, medical history, and the reason for your visit, here is a general overview of what you can expect during a typical gynecological exam:
- Check-In and Medical History Review:
- You will start by checking in at the clinic or office. The medical staff may ask you to complete paperwork, including a medical history questionnaire, or you may have provided this information in advance.
- Discussion with the Healthcare Provider:
- You will have a conversation with the gynecologist or healthcare provider to discuss your medical history, any specific concerns or symptoms you may be experiencing, your menstrual cycle, sexual activity, contraception use, and any relevant family history.
- Physical Examination:
- The physical examination typically includes:
- General Physical Exam: This may involve checking your blood pressure, weight, and overall health.
- Breast Exam: The healthcare provider will examine your breasts for any lumps, changes, or abnormalities.
- Abdominal Exam: They may gently press on your abdomen to check for any tenderness or abnormalities.
- The physical examination typically includes:
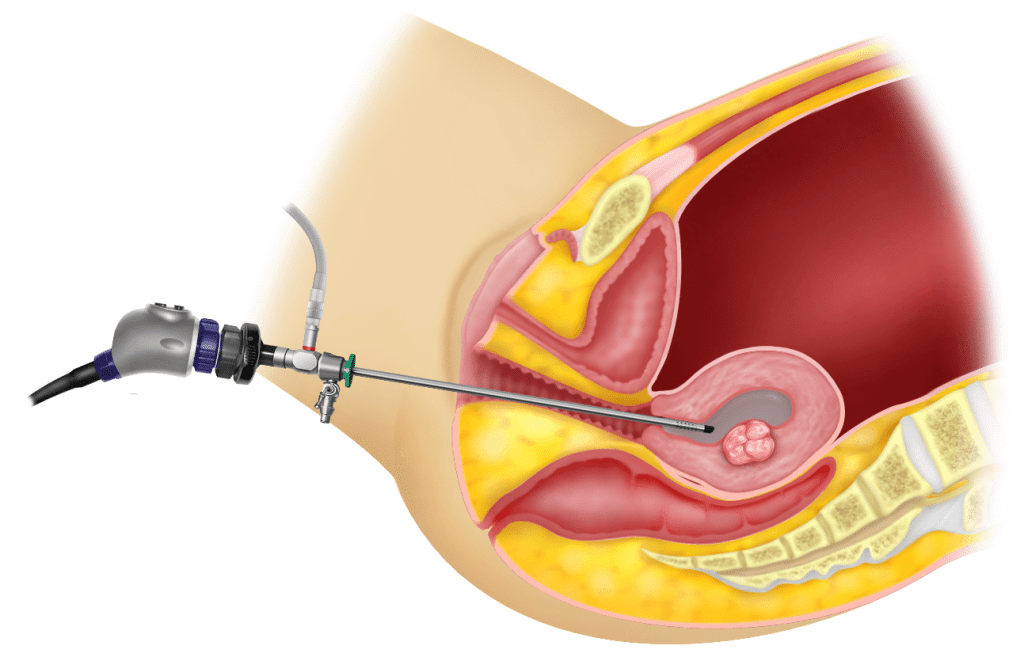
- Pelvic Examination:
- A pelvic exam involves the following steps:
- External Examination: You’ll be asked to undress from the waist down and lie on the examination table with your feet in stirrups. The healthcare provider will first perform an external examination to check for any abnormalities or visible signs of infection.
- Speculum Examination: A speculum (a plastic or metal instrument) is gently inserted into the vagina to hold it open, allowing the healthcare provider to view the cervix and vaginal walls. This may cause some mild discomfort or pressure.
- Pap Smear (if needed): During the speculum exam, the healthcare provider may collect cells from the cervix for a Pap smear (Pap test). This test screens for cervical cancer or precancerous changes in the cervix.
- Bimanual Examination: The provider may perform a bimanual examination by inserting one or two gloved fingers into the vagina while gently pressing on the lower abdomen. This allows them to assess the size and position of the reproductive organs, such as the uterus and ovaries.
- A pelvic exam involves the following steps:
- Discussion of Findings and Recommendations:
- After the examination, your healthcare provider will discuss their findings with you, answer any questions you may have, and provide recommendations for further care or screenings, if necessary. This may include discussions about birth control, STI testing, or other aspects of your reproductive health.
- Follow-Up and Next Steps:
- Depending on the results of the exam and any specific concerns identified, your healthcare provider may recommend follow-up appointments, additional tests, or treatments.
It’s essential to communicate openly with your healthcare provider throughout the process. If you feel uncomfortable or experience pain during any part of the exam, don’t hesitate to let your provider know. They can make adjustments to minimize discomfort and ensure you have a positive experience while receiving essential care for your reproductive health.
Consult, personalized advice and guidance from Dr. Arohi Tasgaonkar, a Gynecologist in Manpada at in Complete Women’s Care