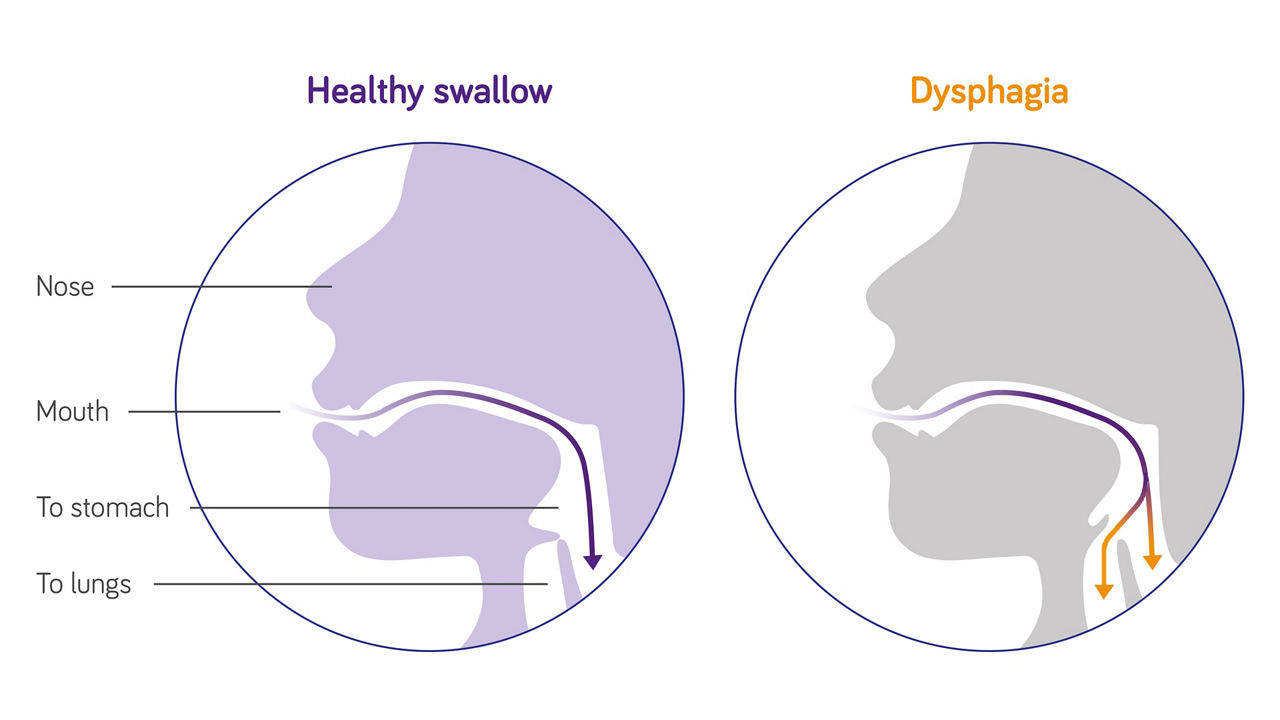
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, can result from various underlying causes. The common causes of dysphagia include:
1. Muscular Problems:
– Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles involved in swallowing can make it difficult to move food and liquids through the throat and into the esophagus. Conditions like myasthenia gravis or muscular dystrophy can lead to muscle weakness.
– Neuromuscular Disorders:Neurological conditions that affect the nerves controlling swallowing muscles, such as Parkinson’s disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), can cause dysphagia.
2. Structural Issues:
– Esophageal Strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus due to scarring, inflammation, or the presence of benign or malignant tumors can obstruct the passage of food and cause difficulty swallowing.
– Achalasia: This is a disorder of the lower esophageal sphincter (the muscular ring that separates the esophagus from the stomach), causing it to fail to relax properly and allow food to pass into the stomach.
– Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):Severe GERD can lead to inflammation and scarring of the esophagus, which can result in dysphagia.
3. Neurological Disorders:
– Stroke: Stroke can damage the brain’s control over swallowing muscles, leading to dysphagia.
– Multiple Sclerosis: This neurological condition can affect nerve signals involved in swallowing.
– Brain Injury: Traumatic brain injuries or other brain disorders can disrupt the coordination of the swallowing process.
4. Psychological Factors:
– Anxiety and Stress: Psychological factors, such as anxiety or stress, can sometimes lead to functional dysphagia, where there is no physical obstruction but the perception of difficulty swallowing.
5. Infections and Inflammation:
– sophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus due to infections, allergies, or irritation from medications can cause pain and difficulty swallowing.
– Throat Infections: Infections in the throat, like tonsillitis or strep throat, can make swallowing painful and difficult.
6. Radiation Therapy or Surgery: Treatments for head and neck cancers, such as radiation therapy and certain surgical procedures, can lead to damage or scarring that affects swallowing.
7. Medications: Some medications, especially those that cause dry mouth as a side effect, can make swallowing more challenging.
8. Age-Related Changes: As people age, changes in the muscles and tissues involved in swallowing can contribute to dysphagia.
9. Eating and Drinking Habits: Eating too quickly or not chewing food thoroughly can lead to swallowing difficulties, especially in children.
10. Foreign Bodies: Accidentally swallowing objects or food that is too large can cause choking and dysphagia.
11. Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like eosinophilic esophagitis, an autoimmune disorder, can cause inflammation and narrowing of the esophagus, leading to difficulty swallowing.
It’s important to note that the treatment and management of dysphagiadepend on the underlying cause. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent difficulty swallowing, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
For more information, consult Dr. Vedant Karvir the Best Gastroenterologist in Mumbai Practicing at Globus Gastroenterology Hospital.