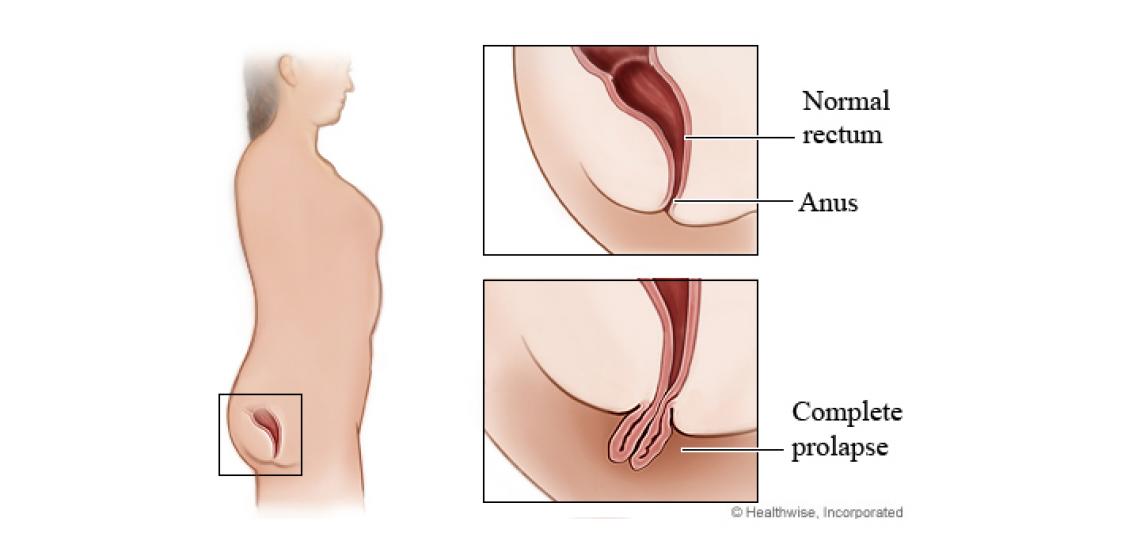
Rectal prolapse is a medical condition where the rectum, which is the last part of the large intestine, protrudes out of the anus. It can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Weakness of Pelvic Muscles and Ligaments: One of the primary causes of rectal prolapse is the weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments that support the rectum. This weakening can result from aging, childbirth, repeated heavy lifting, or chronic straining during bowel movements.
2. Chronic Constipation: Long-term constipation and the habit of straining during bowel movements can lead to increased pressure on the rectum. This pressure can contribute to the development of rectal prolapse over time.
3. Chronic Diarrhea: Frequent and severe diarrhea can also strain the rectum and weaken the supporting structures, potentially increasing the risk of rectal prolapse.
4. Aging: As people age, the tissues and muscles in the pelvic area may naturally weaken, making them more susceptible to rectal prolapse.
5. Childbirth: In women, the process of childbirth, especially if it involves difficult or prolonged labor, can cause damage to the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments, increasing the risk of rectal prolapse.
6. Previous Rectal Surgery: Individuals who have undergone previous rectal or pelvic surgery may be at a higher risk of developing rectal prolapse due to potential disruption of supporting structures during surgery.
7. Neurological Conditions: Certain neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injury, can affect the normal functioning of the pelvic muscles and nerves, potentially contributing to rectal prolapse.
8. Connective Tissue Disorders: Some connective tissue disorders, like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome, can weaken the connective tissues in the pelvic area, increasing the likelihood of rectal prolapse.
It’s important to note that rectal prolapse can vary in severity, and some individuals may have a combination of factors contributing to their condition. The specific cause and risk factors can vary from person to person. If you suspect you have rectal prolapse or are experiencing symptoms related to it, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis from a healthcare professional, such as a colorectal surgeon or gastroenterologist. Treatment options will depend on the severity of the prolapse and the underlying causes.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with rectal prolapse, consult Dr. Chintamani Godbole one of the best Colorectal Surgeon in Mumbai